Smart shape
What is smart shape? In DGM.js, we call smart shape that can be scripted, have extended properties, and can have constraints. All primitive shapes are smart shapes.
- extended properties allows to define additional metadata of the shapes.
- constraints allows to define the behaviors of the shape. (e.g. aligning, sizing, styling, …)
- scripts allows to define how to draw or outline of the shape.
By combining the above three things, you can create complex and special shapes. For example, it is possible to define shape elements for UML Class Diagram, Sequence Diagram, UI Wireframe or whatever.
Extended Properties
You can define additional metadata of the shapes by creating extended properties. Each extended property should have it’s name and type. Here are the types of extended properties you can create:
- string
- number
- boolean
- enum
- text (multi-lines)
The extended properties can be used in constraints and scripts.
Constraints
Constraint can be used to impose specific constraints on a shape. Followings are the supported constraint types for a shape:
- align-children
- align-to-parent
- anchor-on-parent
- inherit-styles
- adjust-route
- set-state-from-property
- set-size
- set-line
- fill-text
align-children
This constraint aligns children shapes.
- orient :
top,bottom,middle,left,right,center,vert-fill,horz-fill. - align :
left,left-outside,left-border,center,right,right-outside,right-border,top,top-border,top-outside,middle,bottom,bottom-border,bottom-outside,fill. - query : Align only the matched children shapes. For example, if the query is
#compartment, aligns only the children shapes which has#compartmenttag. For more about query expression, see Query. - gap : A gap value among the children.
- fillLast : Fill the last child shape.

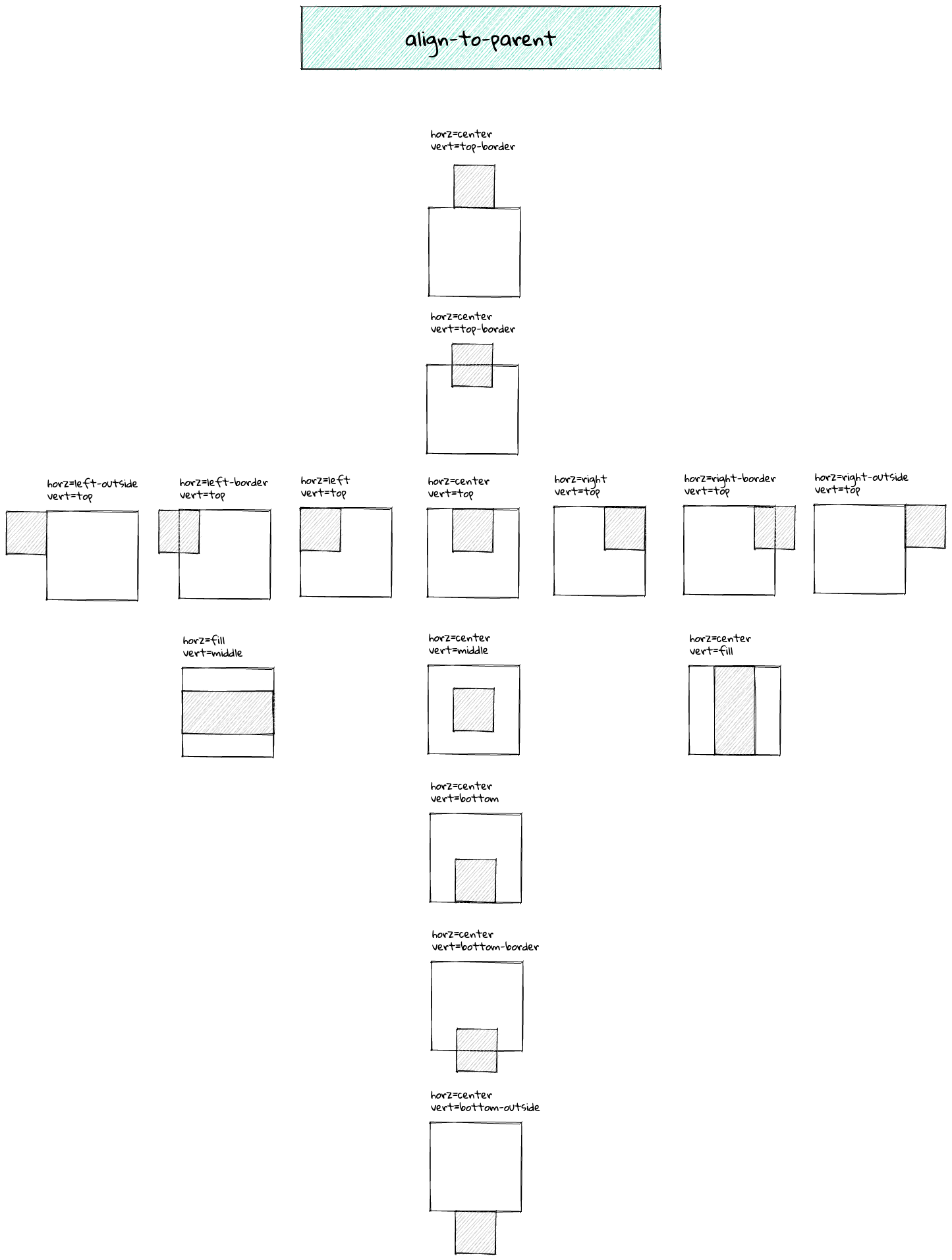
align-to-parent
This constraint aligns the shape relative to its parent.
- horz :
none,left,left-outside,left-border,right,right-outside,right-border,center,border,outside,fill. - vert :
none,top,top-border,top-outside,bottom,bottom-border,bottom-outside,middle,border,outside,fill. - horzOffset : Horizontal offset.
- vertOffset : Vertical offset.
- query : A query for determining the parent to which the constraint should be applied. For more about query expression, see Query.
- innerArea : Align to parent’s inner area. It means that parent’s padding values are used for aligning.
anchor-on-parent
This constraint makes an anchor to the it’s parent. When the parent shape moves, the anchored shape also move along. This is used for the text shape which is attached to a connector.
inherit-styles
This constraint inherits styles automatically from it’s parent shape.
- opacity : Inherit opacity.
- stroke : Inherit stroke styles.
- fill : Inherit fill styles.
- font : Inherit font styles.
- textAlignment : : Inherit text alignments.
- query : A query for determining the parent to which the constraint should be applied. For more about query expression, see Query.
adjust-route
This constraint automatically adjust route of a connector. This is used for routing a connector.
set-state-from-property
This constraint automatically changes a state of the shape.
- property : An extended property to be used as state value.
- expression : A script expression to be used as state value. You can use
valuefor the extended property value in the expression. (e.g.(if value "$background" "$foreground")) - query : Query to find a shape from children to change state. For more about query expression, see Query.
- state : State to change:
enable,visible,rotatable,connectable,containable,opacity,roughness,width,height,rotate,padding,corners,borders,borderPosition,strokeColor,strokeWidth,strokePattern,fillColor,fillStyle,fontColor,fontSize,fontStyle,fontWeight,shadow,shadowColor,shadowOffset,text,horzAlign,vertAlign,wordWrap,lineHeight,paragraphSpacing,lineType,headEndType,tailEndType.
size-size
This constraint automatically changes the size of the shape.
- width :
ignore,children,text,text-min,parent,value. - height :
ignore,children,text,text-min,parent,value. - widthValue : The actual value when width is
value. - heightValue : The actual value when height is
value.
set-line
This constraint automatically changes the form of a line shape.
- type :
free,horzontal,vertical.
fill-text
This constraint automatically fills the shape with the provided text or lorem ipsum text, adjusting the text length to fit the size of the shape.
- text : Text string value to fill. (If empty, lorem ipsum text will be used)
Scripts
User can redefine of shape’s default behaviors how to rendering and outlining. The followings are supported script types of a shape:
- render
- outline
- viewport
For detailed information about the script language, please refer to Script Language.
render
The script bound to render should code how to draw the shape. The below code is to draw a triagle inside a box.
(do (def! l (. shape :left)) (def! r (. shape :right)) (def! t (. shape :top)) (def! b (. shape :bottom)) (def! xc (/ (+ l r) 2)) (def! seed (. shape :getSeed)) (. canvas :polygon [[xc t] [r b] [l b]] seed) (. shape :renderText canvas))You can use the shape’s default rendering behavor. The below code is draw the cross mark over the rectangle’s default rendering.
(do (def! l (. shape :left)) (def! r (. shape :right)) (def! t (. shape :top)) (def! b (. shape :bottom)) (def! seed (. shape :getSeed)) (. shape :renderDefault canvas) (. canvas :line l t r b seed) (. canvas :line r t l b seed))outline
The script bound to outline should express a vector of points that constitutes the outline of the shape. The below is to define the outline of a triangle.
(do (def! l (. shape :left)) (def! r (. shape :right)) (def! t (. shape :top)) (def! b (. shape :bottom)) (def! xc (/ (+ l r) 2)) [[xc t] [r b] [l b] [xc t]])viewport
The script bound to outline should express the area of the shape’s viewport. The viewport of shape is the area where the shape is rendered. Shapes are sometimes drawn beyond the bounding box, and the viewport must contain all of this area. Otherwise, any area beyond the viewport will be cropped when the image is exported.
(do (def! l (. shape :left)) (def! r (. shape :right)) (def! t (. shape :top)) (def! b (. shape :bottom)) (def! g 10) [[(- l g) (- t g)] [(+ r g) (+ b g)]])More features
In addition to extended properties, constraints, and scripts, there are other properties that can adjust the characteristics of a shape.
Sizable
The sizable property specifies the method for adjusting the size of the shape. You can choose one from:
none: The shape cannot be sizable.horz: Only the width of the shape can be sizable.vert: Only the height of the shape can be sizable.free: The shape can be sizable freely both width and height.ratio: The shape can be sizable while maintaining the aspect ratio.
Movable
The movable property specifies the method for moving the shape. You can choose one from:
none: The shape cannot be movable.horz: The shape can be movable horizontal only.vert: The shape can be movable vertical only.free: The shape can be movable freely.parent: The shape can be movable with it’s parent shape.
If movable is parent and you want it to operate only on a specific type of parent, you can write a query in movableParentFilter.
Containable
The containable property indicates that the shape can contain other shapes inside it. To specify what kind of shapes can be contained, you can write a query expression in the containableFilter.
Text editable
The textEditable property specifies whether the user can edit the text of the shape.
Path editable
The pathEditable property specifies whether the user can edit the path points of the line shape.
Anchored
The anchored property indicates the shape is anchored on another shape.
Connectable
The connectable property indicates the shape can be connected by connectors.
Query
You can use query expression to filter shapes.The syntax of query expression can be defined as below.
<query> = <clause>["|" <clause>]*<clause> = <term>["&" <term>]*<term> = <name-selector> | <type-selector> | <tag-selector><name-selector> = <name> e.g.) OuterBox, TextName, ...<type-selector> = "@"<type> e.g.) @Box, @Text, @Line, ...<tag-selector> = "#"<tag> e.g.) #label, #compartment, ...Here are some examples of query expressions:
Foo: All shapes whose name isFoo.@Text: All shapes whose type is Text.#compartment: All shapes having acompartmenttag.Bar&@Line: All shapes whose name isBarand type is Line.@Box|Baz|@Text&#compartmentAll shapes whose type is Box or name isBazor type is Text with acompartmenttag.